CAR T cell therapy targeting CD19 has emerged to show spectacular success in the treatment of B leukemias and lymphomas. This strategy is mainly achieved by potentiating T-cells to recognize and target tumor cells. However, CD19 CAR T cell therapy can result in neurotoxicity 1 and cytokine-associated toxicity as well as relapse with antigen dim or negative disease 2; therefore, strategies to mitigate these side effects are needed.
Recent trials in adults with lymphoma using fully human CAR (Hu19-28) T cells resulted in the secretion of lower levels of cytokines and conferred lower neurologic toxicity. 3 To assess the potential responsiveness of this Hu19-28 CAR T cells against B-acute lymphocytic leukemia (B-ALL), T cells engineered with the Hu19-28 CAR were compared with murine FMC63-based CARs. Hu19-28 and FMC63-based CAR T cells exhibited a rapid increase in IFNg secretion in response to the CD19 + NALM6 ALL cell line (CD19 High). Interestingly, and consistent with the lower toxicity of Hu19-28 CAR T cells in patients with lymphoma, IFNg secretion by Hu19-28 CAR T cells in response to a CD19 Low NALM6 line was significantly reduced as compared to FMC63-28 CAR T cells. Hu19-28 CAR T cells also exhibited high in vitro cytotoxicity against CD19 High NALM6. Notably though, Hu19-28 CAR T cells demonstrated lower in vitro cytotoxicity against CD19 Low NALM6 as compared to FMC63-28 CAR T cells. These important differences were also detected in vivo; both Hu19-28 and FMC63-28 CAR T cells eradicated CD19 High leukemia in an NSG mouse model but only the latter efficiently controlled the in vivo growth of CD19 Med leukemia.
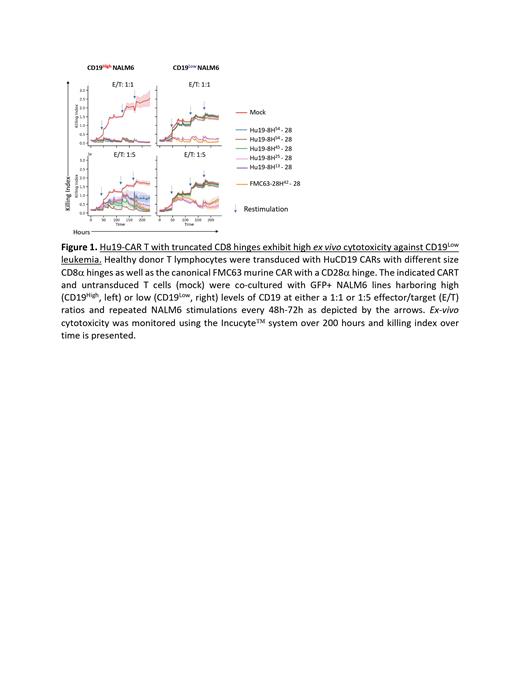
As we and others have shown that the hinge domain of the CAR plays a critical role in its function, especially against low antigen density tumors 4,5,6, we evaluated the impact of the hinge on the function of the Hu19-28 CAR T cells. Compared with the initial construct with a CD8a hinge length of 54 amino acids (Hu19-8H 54-28), Hu19 constructs with 45 (Hu19-H 45-28), 25 (Hu19-H 25-28), and 13 (Hu19-8H 13-28) amino acids were generated. All CAR constructs were highly expressed at the surface of transduced T lymphocytes and were efficient in the killing of CD19 High leukemia. However, only the Hu19-H 25-28 and Hu19-8H 13-28 CAR constructs exhibited high cytotoxicity against CD19 Low leukemia ( Figure 1). Together these data support the preclinical evaluation of Hu19-28 CAR constructs with shorter CD8a hinge lengths for the treatment of pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory ALL.
References
1. Gust J et al (2018) CNS Drugs, 32(12) 1091-1101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-018-0582-9
2. Lee DW et al (2019) Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, 25(4) 625-638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.12.758
3. Brudno JN et al (2020). Nature Medicine, 26(2) 270-280. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0737-3
4. Majzner RG et al (2020) Cancer Discovery, 10(5), 702-723. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0945
Chen X/ Mirazee JM et al (2022) Journal of Magnetic Resonance 340, 107234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2022.107234
Mirazee et al., in preparation
Disclosures
Kochenderfer:Kite, a Gilead company: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Shah:Lentigen: Research Funding; CARGO: Consultancy; VOR: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunoadoptive Cell Therapy Private Limited: Consultancy, Other: Scientific Advisory Board.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal